In the world of modern technology, few innovations have garnered as much attention and excitement as blockchain. Initially known as the underlying technology behind Bitcoin, blockchain has since evolved into a revolutionary force with the potential to transform industries far beyond finance. For beginners curious about this groundbreaking technology, this article serves as an in-depth introduction to understanding blockchain, its fundamental concepts, applications, and implications.
What is Blockchain?
At its core, blockchain is a decentralized, distributed ledger technology that records transactions across multiple computers in a way that is secure, transparent, and immutable. Unlike traditional centralized systems where data is stored in a single location, blockchain operates on a network of nodes, each maintaining a copy of the ledger. This distributed nature ensures that no single entity controls the data, making it resistant to tampering and censorship.
How Does Blockchain Work?
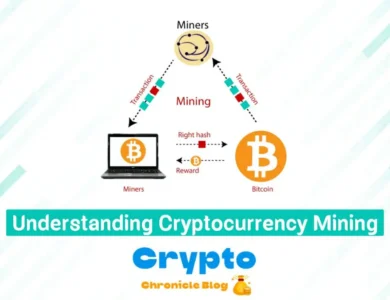
Blockchain operates through a series of interconnected blocks, each containing a list of transactions. These blocks are linked together in a chronological sequence, forming a chain. When a new transaction occurs, it is verified by network participants known as miners, who use cryptographic algorithms to validate the transaction and add it to a block. Once added, the block is appended to the existing chain, creating a permanent and transparent record of the transaction history.
Key Components of Blockchain
- Decentralization: Unlike centralized systems, blockchain operates without a central authority, allowing for greater transparency and resilience against censorship and single points of failure.
- Immutability: Once data is recorded on the blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted, ensuring the integrity and trustworthiness of the ledger.
- Consensus Mechanisms: Blockchain networks rely on consensus mechanisms to validate transactions and maintain the integrity of the ledger. Popular consensus algorithms include Proof of Work (PoW), Proof of Stake (PoS), and Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS).
- Cryptographic Security: Blockchain employs cryptographic techniques such as hashing and digital signatures to secure transactions and prevent unauthorized access.
Applications of Blockchain
- Cryptocurrencies: Bitcoin, the first cryptocurrency, introduced blockchain technology to the world. Since then, numerous cryptocurrencies have been developed, each with its own use cases and features.
- Smart Contracts: Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. They enable automated and transparent transactions without the need for intermediaries.
- Supply Chain Management: Blockchain can be used to track and trace products throughout the supply chain, enhancing transparency, efficiency, and accountability.
- Identity Management: Blockchain-based identity solutions offer secure and decentralized methods for managing digital identities, reducing the risk of identity theft and fraud.
- Voting Systems: Blockchain can revolutionize voting systems by providing secure, transparent, and tamper-resistant platforms for conducting elections.
Challenges and Considerations
While blockchain holds immense promise, it also faces several challenges and considerations, including scalability, interoperability, regulatory uncertainty, and energy consumption. Addressing these challenges will be essential for realizing the full potential of blockchain technology and fostering its widespread adoption.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology represents a paradigm shift in how we store, manage, and transact data. Its decentralized and transparent nature has the potential to revolutionize industries ranging from finance and supply chain to healthcare and governance. As we continue to explore the possibilities of blockchain, it is crucial for beginners to grasp its fundamental concepts, applications, and challenges. By understanding blockchain technology, individuals can better navigate the evolving landscape of the digital economy and contribute to its ongoing development and innovation.
Sources and References:
Naturally, here are some sites that may be useful to you: